(a) (b)
Figure 1. (a) Location of Lebanon in the Mediterranean, and (b) the study area of Lebanon.
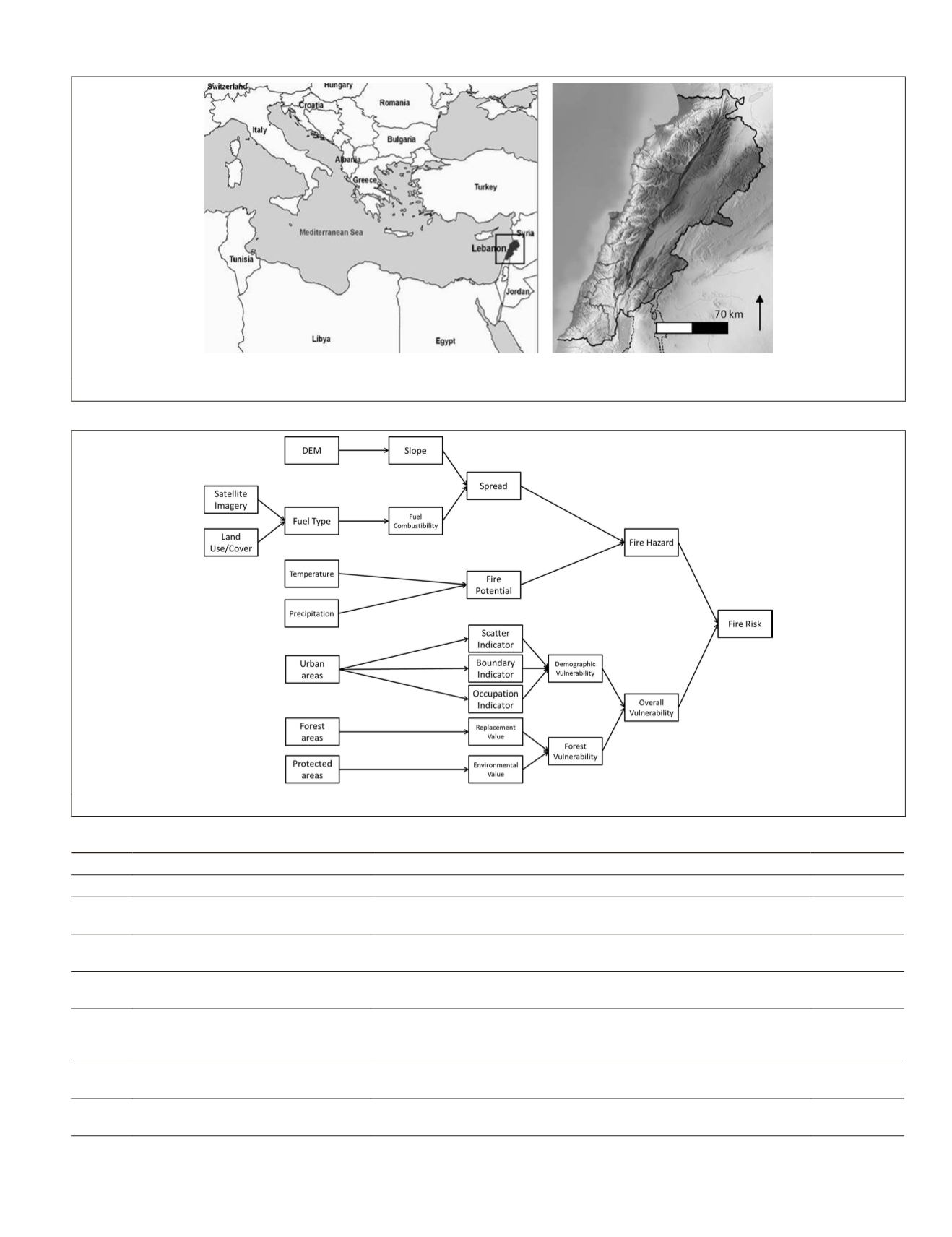
Figure 2. Flowchart of the methodology of work.
T
able
1. T
he
P
rometheus
F
uel
T
ype
C
lasses
and
their
C
orresponding
C
ombustibility
L
evels
Fuel type % Coverage
Description
Combustibility
1
Ground fuels (cover > 50%)
Grass
High
2
Surface fuels
(shrub cover > 60%; tree cover < 50%)
Grassland, shrubland (smaller than 0.3-0.6 m and with a high percentage
of grassland), and clear-cuts, where slash was not removed.
Moderate
3
Medium-height shrubs
(shrub cover > 60%; tree cover < 50%)
Shrubs between 0.6 and 2.0 m
High
4
Tall shrubs (shrub cover > 60%;
tree cover <50%)
High shrubs (between 2.0 and 4.0 m) and young trees resulting from
natural regeneration or forestation.
Very high
5
Tree stands (>4 m) with a clean
ground surface (shrub cover < 30%)
The ground fuel was removed either by prescribed burning or by
mechanical means. This situation may also occur in closed canopies in
which the lack of sunlight inhibits the growth of surface vegetation.
Low
6
Tree stands (>4m) with medium
surface fuels (shrub cover > 30%)
The base of the canopies is well above the surface fuel layer (>0.5 m).
The fuel consists essentially of small shrubs, grass, litter, and duff.
High
7
Tree stands (> 4m) with heavy surface
fuels (shrub cover >30%)
Stands with a very dense surface fuel layer and with a very small vertical
gap to the canopy base (<0.5 m).
High
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING
June 2015
501


